TABLE OF CONTENT
- What is e-commerce fraud?
- Types of e-commerce fraud
- Reasons for e-commerce fraud
- How to identify fraud on e-commerce websites?
- 10 strategies for successful e-commerce fraud prevention
- Manually review risky orders
- Limit order quantities
- Collect proof of delivery
- SSL certificates and encryption
- Show clear policies on your website
- Be vigilant around peak shopping seasons
- Use verification software
- Build a blocklist
- Use IP fraud scoring tools
- Implement fraud detection rules and filters
- Conclusion
A. What is e-commerce fraud?
E-commerce fraud occurs when scammers intervene in a commercial transaction on an online store, aiming for personal or financial gain. Also recognized as payment fraud, this criminal activity involves stealing money from the customer, the merchant, or both.
Given the projected global e-commerce sales of $6.3 trillion in 2024, scammers have ample opportunities to exploit customer data and engage in fraudulent activities. Explore the seven types of e-commerce fraud commonly encountered on online stores below.
B. Types of e-commerce fraud
1. Friendly fraud
Friendly fraud occurs when customers purchase on your e-commerce platform and subsequently initiate a chargeback with their bank. They falsely assert non-delivery, discrepancies in the received item, or cancellation of their order soon after placement. This complaint triggers an investigation, leading to 2.8% of e-commerce orders for enterprise brands resulting in chargebacks. While particularly prevalent in Australia and Canada, friendly fraud accounts for 34% of global fraud attacks.
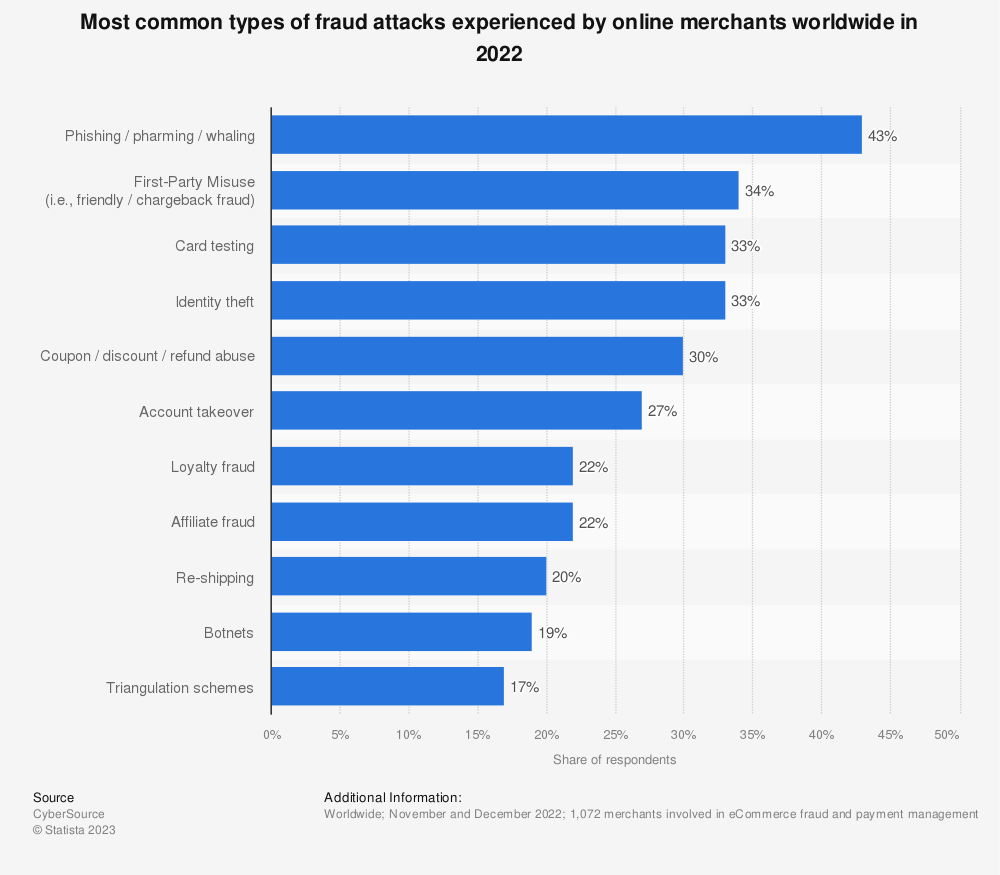
2. Card testing fraud
Card testing is a strategy employed by fraudsters to validate the functionality of a stolen credit card. Typically, scammers initiate a discreet, low-value purchase to avoid detection by the cardholder. Once the card’s viability is confirmed, they proceed to make larger, unauthorized transactions with the stolen card.
Ranked as the third most prevalent form of e-commerce fraud across all merchants, card testing not only poses frustration for customers but also carries potential consequences for your business. A high occurrence of online payments being obstructed due to card testing fraud may lead to additional fees and disputes.
3. Refund abuse
Refund abuse in e-commerce involves customers returning items that are broken, damaged, or stolen to obtain a refund from the retailer.
Despite many merchants having stringent return policies outlining refund eligibility, this remains a costly issue. According to the National Retail Federation, retailers incur a loss of $10.40 for every $100 in returned merchandise due to this fraudulent activity. In 2022, refund abuse experienced the most significant surge in online fraud, with merchants reporting a 56% increase.
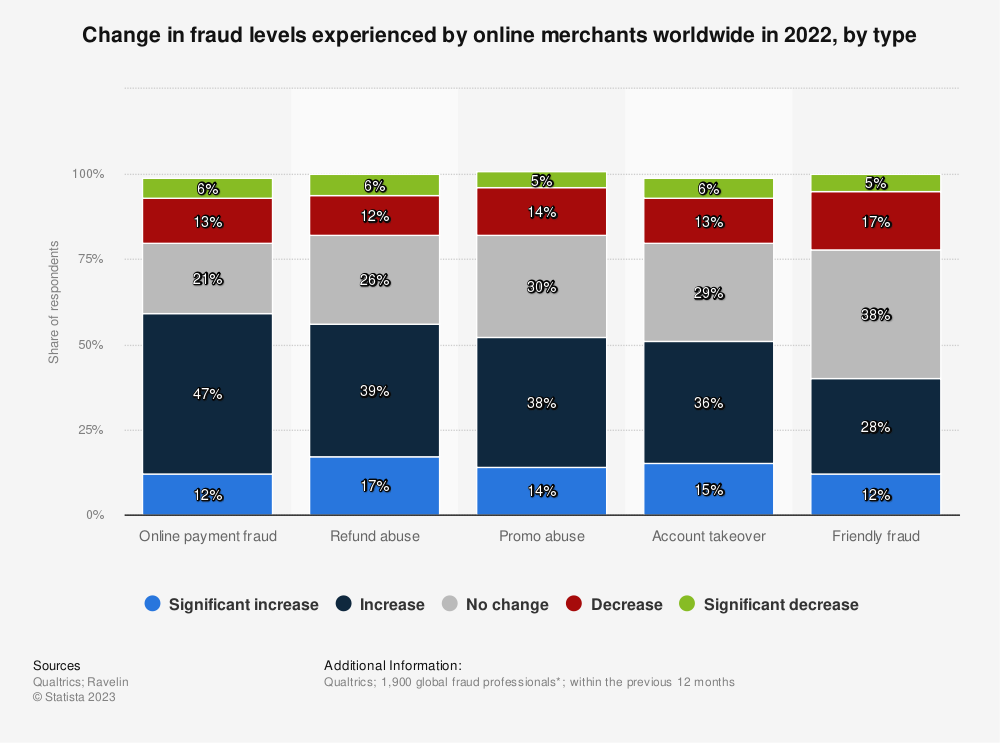
4. Online payment fraud
Online payment fraud commonly referred to as credit card fraud, may also involve scammers duplicating your website to trick customers into unwittingly buying items from a fake site. Perpetrators retrieve funds and store credit card details for potential future scams.
While online payment fraud impacts retailers globally, it is particularly widespread in Canada, where merchants experienced a 71% surge in such incidents last year.
5. Account takeover fraud
Account takeover fraud occurs when scammers illicitly access a customer’s online account and utilize stored payment cards for unauthorized purchases.
In 2022, 51% of surveyed brands reported a rise in account takeover fraud. Scammers typically gain access to customer accounts through weak passwords, phishing emails, or malicious software on the device used for the purchase.
6. Promo, affiliate, or loyalty abuse
E-commerce brands employ promotion, affiliate, and loyalty programs to attract and engage customers, but the widespread use of these programs also attracts scammers who exploit businesses through fraudulent tactics:
- Affiliate Fraud: In affiliate marketing, customers earn a commission for referring friends, but some affiliates abuse this by generating spam traffic or using stolen credit cards to earn commissions, even if the referred customers are not legitimate.
- Loyalty Fraud: Affecting 22% of global retailers, loyalty fraud occurs when customers exploit loyalty programs, earning points through stolen credit cards and then selling these points on the dark web for a percentage of their value.
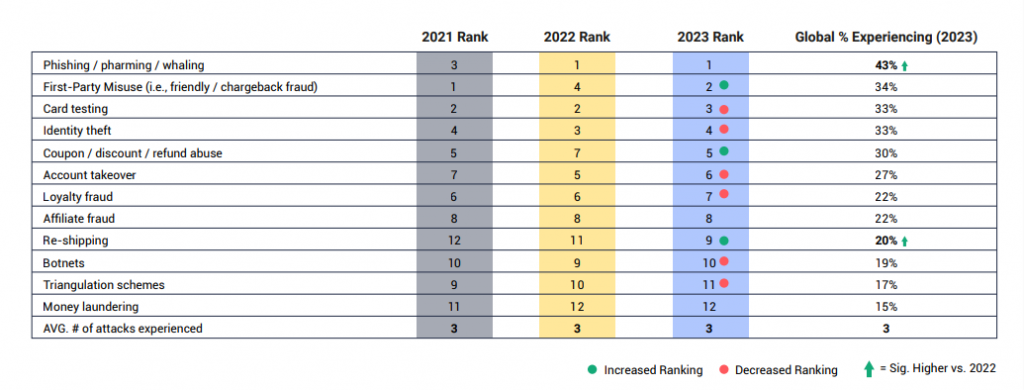
| Sources: cybersource.com
- Promotion Fraud: In 2021, 73% of retailers experienced promo abuse. Scammers exploit loopholes in promotions to claim products for free, undermining the integrity of the retailer’s promotional offerings.
C. Reasons for e-commerce fraud
E-commerce fraud has diverse origins and motivations, with key factors including data breaches, where hackers infiltrate a company’s digital network to steal customer information for fraudulent purposes. Compromised credentials, often obtained through phishing or weak passwords, empower fraudsters to make unauthorized purchases or misappropriate funds. Also, the absence of secure payment verification methods, like two-factor authentication or CVV card verification, makes e-commerce platforms susceptible to fraud involving stolen card information.
Poor website security additionally exposes vulnerabilities, allowing cybercriminals to exploit weaknesses for attacks like SQL injection or malware implantation. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) hence involve intruders gaining prolonged, undetected network access, accumulating customer data over time, and leading to fraud. In addition, the rapid growth of e-commerce attracts fraudsters, particularly targeting new and inexperienced merchants lacking robust security measures. International transactions, carrying increased risk, often circumvent strict domestic fraud prevention measures, while legal complexities make prosecuting fraudsters in different countries challenging.
D. How to identify fraud on e-commerce websites?
E-commerce fraud poses a significant financial challenge, leading to both revenue loss from intercepted online orders and a decline in customer loyalty. Once shoppers fall victim to fraud during a purchase on your website, they are less likely to return. Here are seven indicators to identify potential fraudulent activities on your website:
- Higher Order Volumes: Scammers utilizing stolen credit cards often target high-value items to spend money that isn’t their own.
- Low-Value Orders: Be vigilant for small transactions, particularly around $1, as fraudsters often make low-value purchases to test the validity of stolen card details.
- Different Credit Cards: Multiple purchases by one customer, each using a different credit card, are suspicious and may indicate testing of stolen credit card details.
- Repeated Declined Transactions: If payments repeatedly decline, especially due to security code errors, it raises concerns as fraudsters may lack essential information for using a stolen card.
- Unusual IP Locations: Watch out for multiple orders from the same IP address or suspicious orders from unfamiliar locations. For instance, an attempted high-value order from an IP address in Indonesia, when most customers are in the US, signals potential e-commerce fraud.
- Different Billing and Shipping Addresses: This is common in triangulation fraud, where fraudsters use stolen card details to ship items to legitimate customers.
- PO Box Shipping Addresses: While popular for businesses, PO boxes offer scammers an anonymous location for shipping orders. Exercise caution when shipping numerous orders to a single PO address.
E. 10 strategies for successful e-commerce fraud prevention
Here are ten fraud prevention strategies to minimize the likelihood of fraud happening through your website.
1. Manually review risky orders
E-commerce software is designed to identify potentially risky orders. When an order raises concerns, perform a manual review and, if uncertain about its legitimacy, reach out to the customer for additional information, especially for low-value orders from unfamiliar IP locations. If no response is received, there is a high likelihood that the order was placed using a stolen credit card.
Likewise, analyze a customer’s purchase history to assess the legitimacy of a potentially risky transaction. For example, a deviation in a shopper’s usual pattern, such as placing orders from the US but suddenly purchasing from an IP address in Spain may warrant investigation. If the orders are larger than usual, involve a different credit card, and originate from a different location, there is a strong possibility that the account has been compromised. Accuracy is crucial, as approving a false positive—incorrectly flagging a genuine customer as fraud—jeopardizes the customer experience. If a legitimate online order is declined, it may deter customers from attempting another purchase before seeking alternatives from different merchants.
2. Limit order quantities
An unusually high number of items in an order can indicate potential fraud, particularly when scammers use stolen credit cards for illicit purchases on your e-commerce platform. To mitigate the risk, restrict the quantity of units a customer can purchase, evaluate historical sales data to establish a baseline or “normal” average number of units sold daily and automatically prevent orders from surpassing this typical volume, thereby reducing the likelihood of fraudulent activities on your online store.
3. Collect proof of delivery
Return fraud commonly occurs when customers falsely claim non-receipt of their orders. To address this issue and ensure legitimate claims, collaborate with reliable shipping carriers or third-party logistics providers (3PLs) that offer proof of delivery. Customer signatures or photos of delivered parcels serve as evidence, validating the receipt of items and minimizing fraudulent refund claims.
4. SSL certificates and encryption
SSL certificates and encryption play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data transmitted between a user’s browser and a website’s server. This ensures confidentiality and protection against unauthorized access, tampering, or interception. Here’s how SSL certificates and encryption contribute to securing online communications:
- Authentication: SSL certificates verify a website’s identity, confirming that the domain name is registered with the correct organization. This ensures users are connecting with the legitimate website and not a malicious imposter.
- Encryption: SSL certificates enable the use of encryption algorithms to securely encrypt data transmitted between the user’s browser and the website server. This ensures sensitive information like login credentials, credit card numbers, and personal data remains confidential and immune to interception or unauthorized access.
- Secure Browsing Experience: Websites with SSL certificates display visual cues, such as a padlock icon or a green address bar, signaling to users that the connection is secure. This provides reassurance that their information is protected.
- Compliance: Various industries and regulations, like the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), mandate the use of SSL certificates and encryption when processing credit card information to safeguard sensitive data.
To implement SSL encryption, website owners must acquire a certificate from a trusted certificate authority and install it on their web server. Once installed, the SSL certificate enables the server to establish encrypted connections with users’ browsers, ensuring the security and protection of all transmitted data against unauthorized access.
5. Show clear policies on your website
Policies on your website serve as informative pages outlining how your business operates. Beyond generic terms and conditions, having clear policies is instrumental in combating e-commerce fraud. This encompasses:
- Strong Password Policy: Implementing a robust password policy, in conjunction with two-factor authentication, serves as a deterrent against account takeover fraud.
- Return Policy: Establish a comprehensive return policy to strengthen your position when addressing chargebacks or refund requests. Clearly articulate the criteria for returns, required documentation, and the processing methods, whether it involves a cash refund, exchange, or store credit.
- Promotions and Rewards Policies: Enforce policies regarding promotions and rewards, covering aspects such as limited order quantities and restrictions on the sale of reward points. These policies reinforce adherence to the terms and conditions, acting as a deterrent against e-commerce fraud.
6. Be vigilant around peak shopping seasons
The retail season from Thanksgiving to Black Friday Cyber Monday in 2022 marked the most significant on record, with $35.37 billion in sales, reflecting a 4% increase from 2021, as reported by Adobe Analytics. To safeguard both your and your customers’ finances during these peak shopping times, consider bolstering your investment in fraud prevention solutions. This could involve deploying specialized software or increasing cybersecurity staff to manually review potentially risky orders. Such measures will prove instrumental in mitigating the risks associated with peak fraud season.
7. Use verification software
A clear indicator of potential e-commerce fraud emerges when a customer’s billing, shipping, or card details exhibit inconsistencies. Employ verification software to automatically flag orders displaying this red flag. Utilize features such as:
- Card Number (CVN): Enhance security by making the three or four-digit PIN (CVN) a mandatory field in your e-commerce checkout. This additional layer of security, the most widely used fraud detection feature, adds complexity for scammers who typically rely on the information visible on the front of a credit card.
- Address Verification System (AVS): Validate a customer’s billing address against the card being used. According to Stephen Light, CEO and co-owner of Nolah, AVS is effective in catching fraudsters who employ multiple cards for purchases to a single address.
8. Build a blocklist
Just apprehending a scammer once doesn’t guarantee they won’t become a repeat offender. Fraudsters may attempt to deceive merchants by altering their name, shipping address, or credit card details in the hope of slipping fraudulent orders past detection.
Implemented by nearly a quarter of merchants, blocklists serve as a preventive measure against repeat offenders engaging in fraud through their websites. These lists comprise names, credit card numbers, IP addresses, and shipping addresses identified as potential fraud risks. Any new orders with information matching the blocklist are automatically barred.
While blocklists can proactively prevent the processing of fraudulent orders, caution is essential in their usage. A genuine customer may unknowingly use a credit card previously flagged as fraudulent. Blocking their order without clarification may lead to confusion and frustration, deterring them from future purchases, especially once their request to be removed from a blacklist is granted.
9. Use IP fraud scoring tools
A single individual can engage in multiple forms of fraud utilizing the same computer. Identify these recurrent fraudsters with IP scoring tools like SEON or Scamanalys. These tools analyze an IP address associated with previous fraudulent activities, considering factors such as:
- Location, and cross-referencing it with the country where the card is registered.
- Usage of a VPN to mask their actual location.
- Type of internet service provider, distinguishing between residential and public connections.
Orders originating from an IP address with a high fraud score are flagged, enabling the manual review of potentially risky orders or their automatic blocking.
10. Implement fraud detection rules and filters
These mechanisms involve defining specific criteria and thresholds that signal potential fraud, allowing for the highlighting or blocking of transactions aligning with these parameters. For e-commerce businesses, the operation of fraud detection rules and filters unfolds in the following ways:
- Customizable Rules: Tailor fraud detection rules to your business’s unique risk factors, incorporating elements such as transaction amount, customer demographics, product types, and past fraud patterns. Ensure these rules are scalable to adapt to evolving fraud trends and your business’s changing needs.
- Dynamic Thresholds: Establish dynamic thresholds for various risk indicators, such as transaction amount and frequency or speed controls. This prevents false positives and safeguards legitimate transactions from being incorrectly flagged as fraudulent.
- Real-Time Control: Apply real-time fraud detection filters and rules to promptly identify and address potential threats, minimizing the impact of fraud on your business and customers.
- Machine Learning and AI: Integrate machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms into your fraud detection system. By continuously training these algorithms with historical data, the system evolves to counter new fraud mechanisms, enhancing the accuracy and effectiveness of rules and filters over time.
- Tiered Approach: Employ a comprehensive and robust detection system by combining rules, filters, and additional fraud prevention techniques. These may include IP address tracking, geolocation, device fingerprinting, and multi-factor authentication.
- Regular Verification and Optimization: Periodically assess and analyze the efficacy of your fraud detection rules and filters. Adjust them as needed to address emerging trends, reduce false positives, and minimize impacts on genuine customers.
- Integration with Other Tools: Integrate fraud detection rules and filters with other prevention and risk management tools, such as secure payment platforms, SSL encryption, and customer verification systems. This integration creates a comprehensive and consistent security strategy for your business.
F. Conclusion
In conclusion, safeguarding your e-commerce business against the ever-present threat of fraud is paramount in ensuring not only the integrity of your transactions but also the trust of your customers. The ten methods discussed provide a comprehensive framework for robust e-commerce fraud prevention. By adopting customizable rules, and real-time controls, businesses can create adaptive and resilient defenses. A tiered approach, involving a combination of rules and additional preventive measures, enhances the effectiveness of the overall detection system. Embracing these methods establishes a proactive stance, allowing businesses to navigate the dynamic landscape of fraud risks with confidence, ultimately ensuring a secure and trustworthy environment for both merchants and customers alike.
Contact Wgentech to develop the right strategies for your enterprise!








